Hot-rolled steel is an important material widely used in the industrial sector. Its key characteristic is the high-temperature production process, which creates steel sheets with high hardness and flexibility. Hot-rolled steel has diverse applications and plays a crucial role in many industries.
The following from the composition of hot rolled steel, technology, processing and application of several aspects.
The composition of hot rolled steel:Raw materials and alloy composition
Hot-rolled steel is primarily produced from raw materials like iron ore and carbon. The alloy composition can be adjusted to achieve desired mechanical and physical properties.
Hot-rolled steel manufacturing process
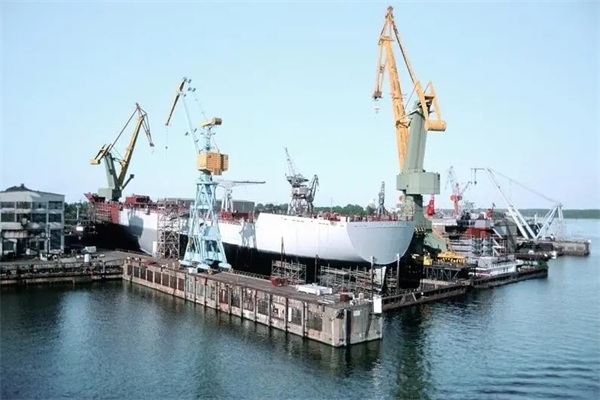
The hot-rolled steel manufacturing process involves iron smelting, steelmaking, hot rolling, and processing. This process ensures the quality and uniformity of hot-rolled steel.
Iron Smelting: The process begins by melting the main raw materials, including iron ore and carbon, in a blast furnace. This process separates impurities from the raw materials and forms molten iron.
Steelmaking: After iron smelting, the molten iron is transferred to a steelmaking furnace to adjust its chemical composition and remove remaining impurities. During this process, other alloying materials may be added to create hot-rolled steel with desired mechanical properties.
Hot Rolling: Once the steelmaking process is complete, the molten steel is poured into holding furnaces to form initial steel slabs. These initial slabs are then transferred to hot rolling units, where they are rolled through rollers to create the final hot-rolled steel sheets. This process requires high pressure and high temperatures to modify the steel’s structure and achieve the desired hardness and flexibility.
Post-Rolling Processing: After being rolled through the rollers, hot-rolled steel sheets may undergo further processing steps to achieve the final size and shape. Post-rolling processing steps may include cutting, bending, welding, and surface treatments.
Heat Treatment and Surface Treatment: Finally, hot-rolled steel sheets may undergo heat treatment and surface treatments to improve their mechanical properties and appearance. These steps can include increasing hardness, enhancing elasticity, cleaning, plating, or painting.
The hot-rolled steel production process is closely controlled and regulated to ensure product quality and uniformity. Process parameters such as temperature, pressure, and rolling speed are adjusted to meet the technical requirements and quality standards of hot-rolled steel.
Processing and heat treatment steps in the production process
After production, hot-rolled steel can undergo various processing and heat treatment steps to create products with desired mechanical properties and shapes.
Uses of hot-rolled steel
Construction Industry: Hot-rolled steel is widely used in the construction industry to manufacture structures, building frames, columns, pipes, and various other applications. Its hardness and flexibility make it an ideal material for construction projects.
Automotive and Transportation Industry: Hot-rolled steel is employed in the production of automobiles, cars, trucks, and other transportation vehicles. Its mechanical properties and resistance to deformation meet the stringent requirements of this industry.
Mechanical and Metalworking Industry: Hot-rolled steel is used in the manufacturing of mechanical parts, metalworking, machinery, and other technical components. Its durability and ease of processing make it an essential material in this industry.
Conclusion
Hot-rolled steel is an important and versatile material in the construction and metalworking industries. Through the production and processing processes, it provides reliable steel plates with good mechanical and physical properties. Hot-rolled steel is widely used in construction, the automotive industry, machinery, and many other industries. The hot-rolled steel industry continues to develop manufacturing and processing technologies, exploring new applications, and discovering potential developments in various industrial and environmental fields.